How VOCs in Paint Affect Indoor Air Quality

- Dec 6, 2024
How VOCs in Paint Affect Indoor Air Quality
Breathing Easy: How VOCs in Paint Affect Indoor Air Quality
Volatile organic compounds, or VOCs, are sneaky substances with a knack for escaping into the air due to their high vapor pressure and low water solubility. These man-made chemicals play a significant role in producing everyday items like paints, pharmaceuticals, and refrigerants.
These are often used as solvents or released as by-products of manufacturing. While they’re essential for many industrial and household applications, their emissions can significantly affect indoor air quality and contribute to health issues.
The Hidden Emissions in Your Paint
The paint on your walls might seem harmless, but it often hides an invisible culprit—VOCs. These sneaky compounds are added to paints to enhance their texture, spreadability, and drying process, ensuring that perfect, smooth finish we all love.
But as the paint dries, VOCs quietly escape into the air in a process called off-gassing, filling your home with that distinct "new paint" smell. The emissions don’t just vanish overnight; they can linger for days, even weeks, subtly impacting your indoor air quality.
Health Risks of VOCs in Paint
When people are exposed to VOCs over time in poorly ventilated spaces, these can have various health implications. Various medical journals have researched on the effects of VOCs on various organ systems of the body. Common examples are:
- Asthma and Bronchitis: VOCs like formaldehyde can irritate the airways, triggering asthma attacks or causing chronic bronchitis, especially in sensitive individuals such as children and those with pre-existing respiratory conditions
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Long-term exposure can worsen symptoms of COPD or contribute to its development in susceptible individuals
- Headaches and Dizziness: Even short-term exposure to high levels of VOCs can cause headaches, dizziness, and nausea, symptoms that are often a precursor to more severe neurological effects with continued exposure
- Dermatitis: Direct exposure to VOCs in products like paint can cause skin irritation and allergic reactions, leading to rashes or dermatitis
In more serious and chronic exposure, there is also a risk for cancer.
- Leukemia and Lymphomas: Long-term exposure to benzene, even at low levels, increases the risk of developing leukemia, especially myelogenous leukemia. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has classified benzene as a Group 1 carcinogen, meaning it is a known cause of cancer in humans.
- Nasopharyngeal Cancer: The National Cancer Institute has reported that individuals who work in industries involving formaldehyde, such as those in the manufacturing of building materials and textiles, have higher rates of nasopharyngeal cancer. Formaldehyde is also implicated in causing other respiratory cancers, especially in people exposed over long periods
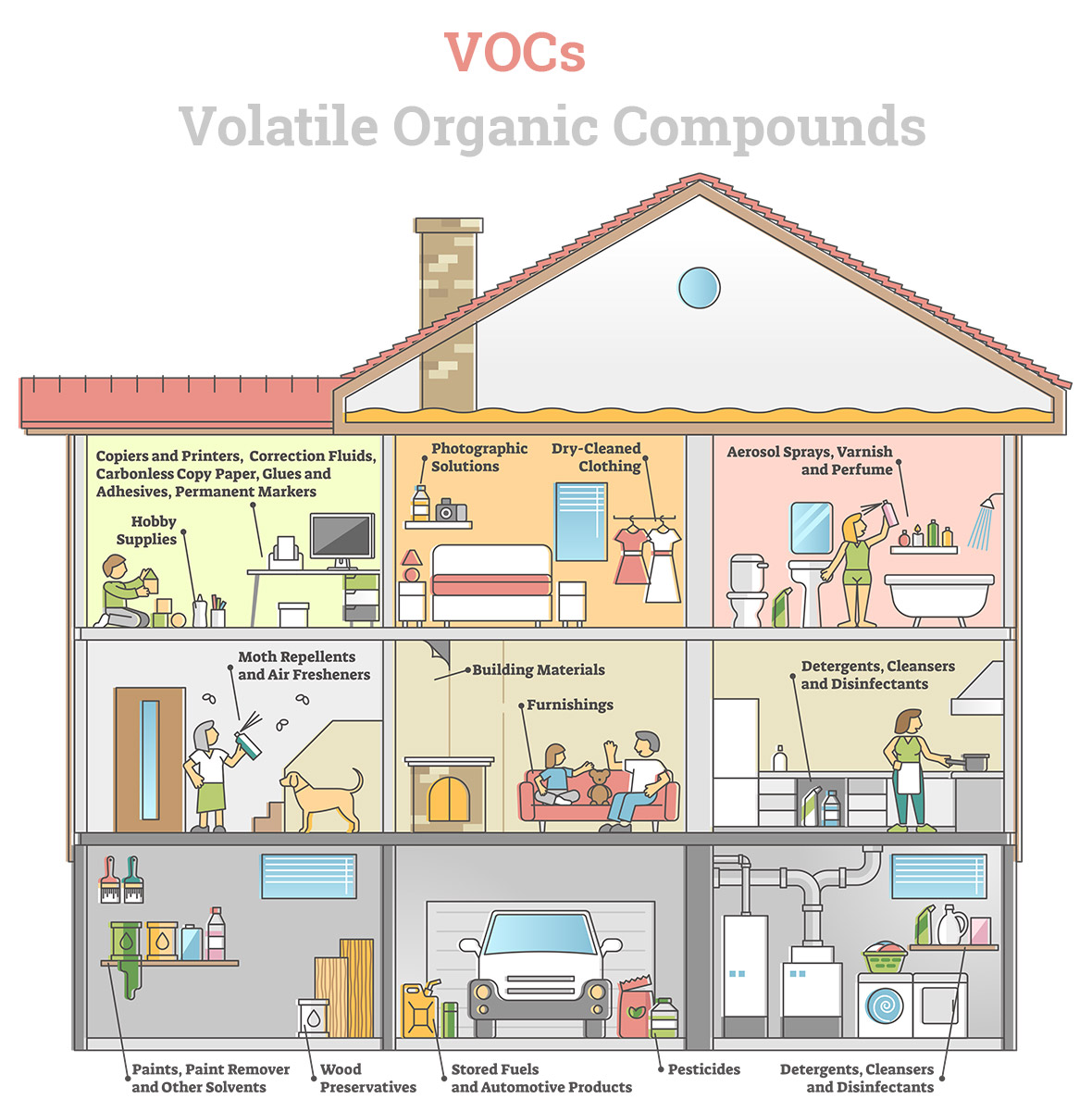
Simple Steps to Kick VOCs Out of Your Home
Reducing VOC exposure in household planning is crucial for both health and environmental reasons. Here are several practical strategies:
1 Choose Low-VOC or VOC-Free Products
When selecting paints, varnishes, and finishes, look for products labeled as "low-VOC" or "zero-VOC." These products release fewer harmful chemicals into the air, reducing both health risks and environmental impact. Many paint brands now offer options with significantly lower VOC content.
2 Ventilate Your Home Properly
Good ventilation is key to reducing indoor VOC concentrations. Open windows, use exhaust fans, and consider installing a ventilation system to improve airflow, especially during and after painting or when using other products containing VOCs. Use ventilation with your air conditioning. This allows VOCs to dissipate more quickly.
3 Use Natural or Non-Toxic Cleaning Products
Household cleaners, air fresheners, and other personal care items can also be significant sources of VOCs. Opt for natural or non-toxic alternatives, such as vinegar, baking soda, or plant-based cleaners, which are free of harmful chemicals.
4 Consider Air Purifiers
Investing in air purifiers with activated carbon filters can help capture VOCs and other pollutants in your home. These devices can be particularly beneficial in high-traffic areas or recently painted rooms. Consider an Ozone Generator.
5 Plan for Eco-Friendly Materials
During home renovations or construction, prioritize the use of eco-friendly, non-toxic materials such as natural wood, cork, and stone, which don't off-gas VOCs. Additionally, opt for carpeting and furniture that are certified low-VOC
6 Minimize Use of Aerosol Sprays
Aerosol sprays, such as those used in air fresheners and cleaning products, release a high concentration of VOCs into the air. Limiting their use can help maintain better indoor air quality.
By making smart choices when planning or updating your home—whether you're renovating, redecorating, or just maintaining it—you can greatly cut down on VOC exposure. This leads to a healthier environment for you and helps protect the planet at the same time.
Final Takeaways
Taking care of your health and the environment go hand in hand. By being mindful of the chemicals we bring into our homes, like the VOCs found in paint and other household products, we can significantly reduce our exposure to harmful toxins.
Not only does this protect our well-being, but it also helps ensure a healthier, cleaner environment for future generations. Making small changes—such as choosing low-VOC paints, improving ventilation, and reducing unnecessary exposure—can go a long way in safeguarding both our health and the planet. After all, a healthier home leads to a healthier you, and a healthier you leads to a healthier world for everyone!
Other Articles
Mar 17, 2023 Plantation Shutters with Shade Sails
Oct 31, 2022 The Path of the Sun
Sep 27, 2021 Timber Clear Coat Broken-down
Aug 20, 2021 Protecting your Floors when Painting
Sep 11, 2020 Door hinges should not be painted
May 25, 2020 Revitalising faded Colorbond Powdercoating
Mar 16, 2020 Painting your front door
Jan 16, 2020 How to Paint a Wall with a Roller
Sep 21, 2018 Repair Walls Gold Coast
Sep 3, 2018 Exterior Timber
Apr 24, 2017 Remodeling Your Home
Apr 7, 2017 Contemporary Design
Mar 17, 2017 House Painted at Southport
Jan 27, 2017 Psychology of Colour
Nov 25, 2016 Before After Beach House Tugun
Nov 13, 2016 Dulux Wash and Wear
Oct 14, 2016 Consider the Light
Aug 8, 2016 Caution with exterior colours
Aug 25, 2015 Value for Money Painting Quotes
Aug 19, 2015 Award Winning Home
May 27, 2015 Green Non Toxic Painters Southport Gold Coast
Apr 16, 2015 Taubmans Certified Painter
Mar 21, 2015 Non Toxic paints
Mar 3, 2015 Colour Consulting Gold Coast
Apr 26, 2014 Care when using Whites
Apr 4, 2014 Re-Painting Timber Doors
Jan 18, 2014 Tilt Slab Duplex Before After
Dec 17, 2013 A change of colour
Jun 6, 2011 Dennis Beck Reference
May 14, 2011 Paintwork for busy areas
Apr 26, 2011 Standing the test of time
Feb 27, 2011 New Environmentally Friendly Paints
May 23, 2009 The Recession & pricing
Aug 9, 2008 Gold Coast Commercial Paintwork
Jan 20, 2007 Feature wall example
